When we think of nuclear power, we often picture massive cooling towers and high-tech control rooms. However, the sector is far more diverse than many realise.
From engineering and radiation safety to cybersecurity and project management, the types of jobs in nuclear industry offer a wide range of career paths for people with varying skill sets.
Regardless of your interests, clean energy innovation or upholding strict safety regulations, this industry offers steady, significant career prospects.
Let’s examine the different functions that ensure the safe and effective operation of this essential energy source.
TRX Summary: Top Jobs in Nuclear Industry
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the diverse career opportunities within the nuclear energy industry. It highlights fourteen essential roles—from nuclear engineering jobs to specialized skilled trades—that sustain carbon-free electricity production.
The guide highlights the critical role these experts play in the worldwide energy industry by examining work responsibilities, safety procedures, and wage benchmarks. It acts as a guide for anyone hoping to establish a secure, lucrative job in a high-tech industry.
Jobs in the Nuclear Industry That are Most In Demand
| Role | Primary Focus | Key Responsibility |
| Nuclear Engineer | Design & Innovation | Designing reactor cores and radiation shielding. |
| Reactor Operator | Plant Operations | Monitoring control rooms and adjusting power output. |
| Radiation Protection Tech | Safety & Monitoring | Checking radiation levels and ensuring protocol safety. |
| Nuclear Technician | Lab & Field Support | Performing chemical analyses and testing for leaks. |
| Nuclear Welder | Precision Trades | Executing high-pressure welds on reactor vessels. |
| Health Physicist | Environmental Safety | Developing safety regulations and emergency plans. |
| Nuclear Chemist | Chemical Integrity | Monitoring water chemistry to prevent corrosion. |
| I&C Engineer | Systems & Data | Maintaining the sensors and control systems. |
| Nuclear Medicine Tech | Healthcare | Administering radioactive drugs for diagnostics. |
| Decommissioning Engineer | Site Restoration | Planning the safe removal of radioactive materials. |
| Waste Management Specialist | Sustainability | Handling and storing spent nuclear fuel safely. |
| Commercial Diver | Underwater Repair | Performing inspections in spent fuel pools. |
| Policy & Regulatory Analyst | Law & Compliance | Shaping international nuclear standards and laws. |
| Materials Scientist | Research & R&D | Studying how materials react to heat and radiation. |
1. Nuclear Engineer
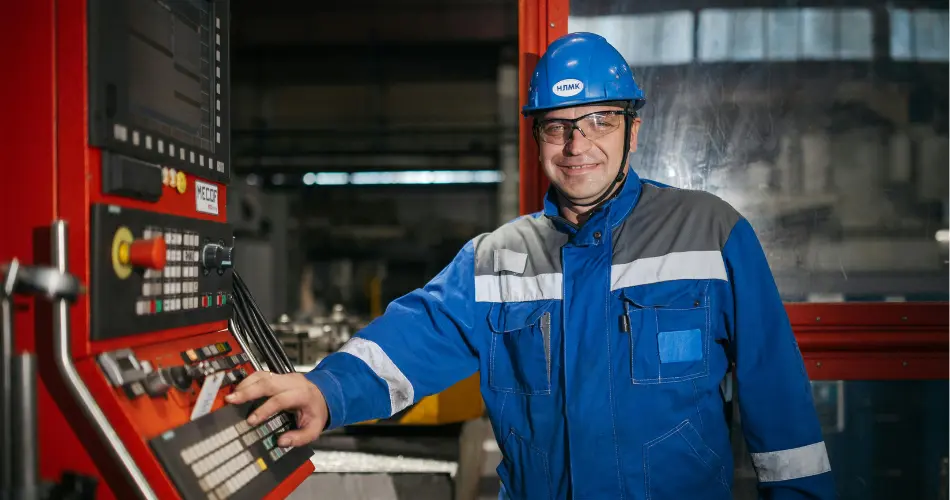

Professionals in nuclear engineering jobs are the primary architects of power generation. They design the reactor core, develop cooling systems, and conduct rigorous safety analysis to prevent accidents. By utilizing advanced nuclear technology, they work to improve the efficiency of plants operating in the United States.
Nuclear engineers often collaborate with firms like Westinghouse to design the next generation of carbon-free energy sources. It is a highly well-paid career path for those interested in nuclear research and complex project management.
- Entry-Level Salary: $85,000 – $105,000
- Experienced Professional: $130,000 – $175,000+
2. Nuclear Power Reactor Operator
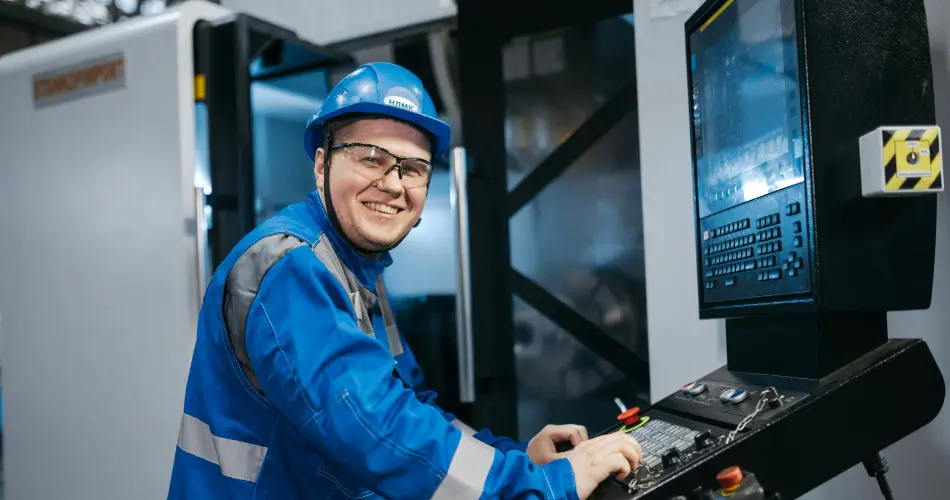

Nuclear power reactor operators control the heart of the nuclear plant. Their role involves starting and stopping the nuclear reactor and adjusting control rods to maintain steady electricity generation.
Because plants run around the clock, operators work in shifts to monitor the turbine and generator systems. This skilled trade requires intense training, often through community colleges or military programs, to verify that all systems ensure compliance with NRC (Nuclear Regulatory Commission) standards.
- Entry-Level Salary: $90,000 – $110,000
- Experienced Professional: $125,000 – $160,000 (plus overtime)
3. Radiation Protection Technician
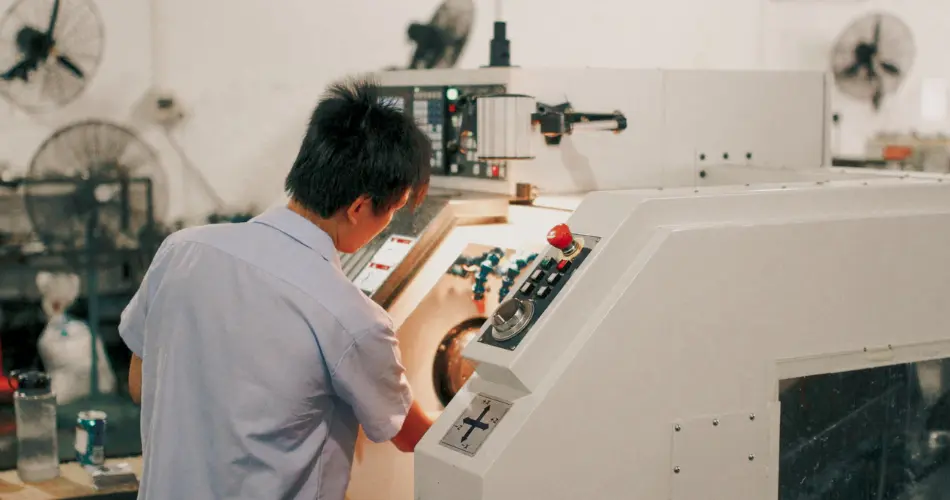

A radiation protection technician (or health physics tech) is essential for health and safety. They monitor radiation exposure for staff and track radioactive material throughout the facility.
During a planned outage, they are critical in surveying areas before maintenance begins. By following strict safety procedures and using checking systems, they protect workers from harm. This is one of the most vital nuclear jobs for maintaining the industry’s rigorous safety record and meeting gov website safety mandates.
- Entry-Level Salary: $60,000 – $80,000
- Experienced Professional: $95,000 – $120,000
4. Nuclear Technician
Working in the energy sector, these technicians troubleshoot and repair electrical equipment and mechanical parts. They assist experienced professionals by performing tests on radioactive materials and monitoring gauge readings.
Many enter the field through an apprenticeship or specific nuclear technology programs. Their work ensures that every inspection is thorough and that the nuclear energy industry remains a reliable source of carbon-free electricity for the public.
- Entry-Level Salary: $55,000 – $75,000
- Experienced Professional: $85,000 – $115,000
5. Nuclear Welder
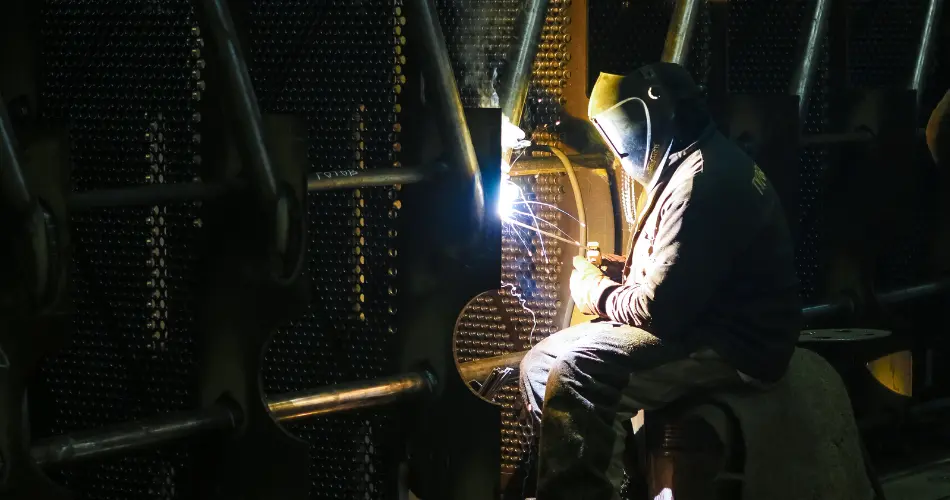

As a highly specialized welder, these individuals perform a skilled trade that is critical during a plant outage or refuel. They weld high-pressure components that must withstand extreme environments.
Using x-ray and ultrasonic testing, they verify the integrity of every joint. This career path is physically demanding but offers some of the highest career opportunities for those in the trades who want to work in nuclear energy.
- Entry-Level Salary: $70,000 – $90,000
- Experienced Professional: $110,000 – $150,000+
6. Health Physicist

Acting as a high-level research scientist, a Health Physicist develops the overarching radiation protection strategies for the entire nuclear plant. They coordinate with the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to ensure compliance and manage long-term safety procedures. Their expertise is required to evaluate seismic risks and environmental impacts, making them indispensable for long-term jobs in the energy industry. They often find a position in government oversight or large-scale utility management.
- Entry-Level Salary: $80,000 – $100,000
- Experienced Professional: $120,000 – $165,000
7. Nuclear Chemist

These experts monitor the chemical balance of the water used in cooling systems to prevent the degradation of the nuclear reactor. By managing radioactive materials in the coolant, they help improve the efficiency of the steam generator. Their work is a blend of nuclear research and practical plant maintenance.
For those looking to work with nuclear energy at a molecular level, this role offers a stable and intellectually rewarding career path.
- Entry-Level Salary: $75,000 – $95,000
- Experienced Professional: $110,000 – $145,000
8. Instrumentation and Control (I&C) Engineer
Focusing on instruments and controls, these engineers design the digital systems that provide data to the reactor operator. They maintain the sensors and electrical equipment that monitor the core and turbine.
If a system fails, they must troubleshoot complex circuits to verify safety. This role is central to the modern nuclear energy industry as plants move toward more automated and digital power generation platforms.
- Entry-Level Salary: $80,000 – $100,000
- Experienced Professional: $115,000 – $155,000
9. Nuclear Medicine Technologist

This career path takes nuclear technology into the healthcare field. These professionals prepare and administer radioactive drugs to patients. They use advanced medical imaging to help doctors diagnose and treat diseases.
While they don’t work in a nuclear plant, their expertise in radiation protection and handling radioactive substances is a specialized branch of nuclear medicine that offers excellent career options in hospitals and clinics.
- Entry-Level Salary: $70,000 – $85,000
- Experienced Professional: $95,000 – $125,000
10. Decommissioning Engineer

As some older plants reach their end-of-life, decommissioning has become a growing sector within nuclear careers. These engineers plan the safe removal of nuclear material and the restoration of the site.
They work closely with the NRC to ensure that all radioactive waste is handled according to the latest gov website guidelines. This role is essential for the energy industry to maintain its status as a clean, carbon-free power source by responsibly closing the loop on plant operations.
- Entry-Level Salary: $85,000 – $105,000
- Experienced Professional: $130,000 – $170,000
11. Nuclear Waste Management Specialist

Managing the lifecycle of nuclear material is a critical long-term job. These specialists develop storage solutions for spent fuel, ensuring it remains isolated from the environment. Their work supports the industry’s goal of providing carbon-free electricity without leaving a negative environmental legacy.
Nuclear waste management specialists often work on secure websites to share sensitive information regarding transport and logistics, ensuring the highest level of security for the u.s. energy grid.
- Entry-Level Salary: $70,000 – $90,000
- Experienced Professional: $110,000 – $145,000
12. Commercial Diver (Nuclear)

This is a highly specialized skilled trade where divers perform inspection and repair work underwater in spent fuel pools or intake structures. They might repair the generator cooling intakes or weld components that are submerged. This role requires extreme focus on health and safety to minimize radiation exposure. It is a unique way to work in nuclear energy for those who enjoy challenging, hands-on environments.
- Daily/Project Rate: $500 – $1,500 per day
- Annual Range: $100,000 – $200,000+ (depending on contracts)
13. Nuclear Policy & Regulatory Analyst

These professionals work primarily with government agencies or the Nuclear Regulatory Commission. They analyze how new laws and international treaties affect power generation. By reviewing data from a gov website, they help shape the future of nuclear energy. This is one of the best career options for those with a background in law or political science who want to contribute to the carbon-free transition at a systemic level.
- Entry-Level Salary: $70,000 – $95,000
- Experienced Professional: $120,000 – $160,000
14. Materials Scientist

Often coming from a mechanical engineer background, these scientists study how metals and composites hold up under intense radiation and seismic stress. Their research is vital for the development of small modular reactors (SMRs), which are the future of the energy sector. By improving the materials used in the core, they help ensure that the next century of nuclear jobs remains centered on safe and efficient technology.
- Entry-Level Salary: $80,000 – $105,000
- Experienced Professional: $125,000 – $170,000
Most Common Questions Related to Jobs in the Nuclear Industry
Careers range from nuclear engineering to specialized skilled trades, focusing on safe, carbon-free electricity production and plant maintenance.
Engineers design and optimize the nuclear plant systems that generate massive amounts of power without emitting greenhouse gases.
Most nuclear jobs require a STEM degree, though many technical roles value apprenticeships and specialized military training.
Yes, the global push for carbon-free power ensures steady demand for professionals to manage aging and new reactors.
The NRC sets the strict safety and operational standards that every professional in nuclear engineering must rigorously follow.
You directly support global climate goals by providing reliable, carbon-free energy while enjoying competitive, well-paid salary packages.
End Note
The nuclear sector is far more than just a source of power; it is a hub of innovation and long-term career stability. As the world pivots toward a carbon-free future, the demand for diverse talent—from engineers to skilled tradespeople—will only continue to grow.
The positions in the nuclear business provide a fulfilling method to have a real impact on the environment, regardless of whether you are just starting out or looking to move.